Hello! There are wonders of space, but you can never know all of them. This time, I’ll tell you a lot about it!
CONTENTS:
The Solar System
The Sun
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Asteroid Belt
Kuiper Belt
Oort Cloud
Moons
Stars and Black Holes
The Birth and Death of a Sun
Black Holes
Supermassive Black Holes
Neutron Stars
Our Sun’s Life
Clusters
Galaxy Clusters
Sun Clusters
Galaxies
Galaxy Collisions
Our Galaxy – The Milky Way
Space Exploration
The History of Space Exploration
The Challenges of Space Travel
Future Missions and Technologies
unfortunately, this book does not contain “space exploration”, nor all the contents inside of it. (which are the history of space exploration, the challenges of space travel, future missions and technologies) if you want it here, you can request me to add it in using the comments below if you want this mindblowing category to be added! SO, you have a chance to change this book! don’t miss out on this oustanding offer! also, please consider subscribing to my website! you can find it in the subscribe page! if you’re having trouble finding the subscribe page, you can comment on one of my posts, like this one, and tell me the problem. you can also tell me other problems that are occuring on the site if you want using comments of any type of post!
The Big Bang
_____________________________________________
The Solar System
The solar system is a vast place, not to say the universe itself. Without further ado, we Start with The Sun.
The Sun
The Sun can fit a million earths inside, and 99.98% of the solar system’s mass in the Sun. Our Sun will turn into a white dwarf at the end of its life.

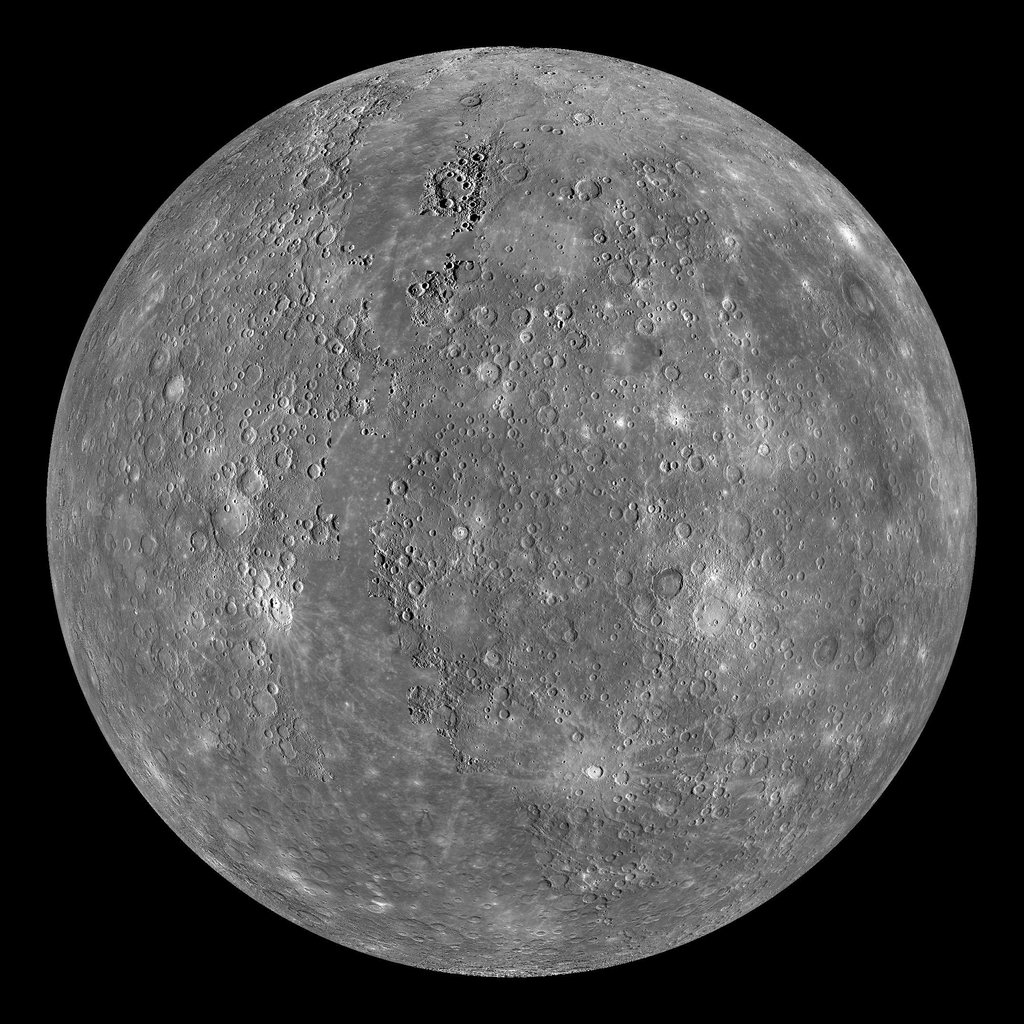
Mercury
Next, it’s the closest planet to the Sun. Its name is Mercury. By far the smallest planet in our solar system, that means its gravity is less strong than earth, making you weigh less than on earth.

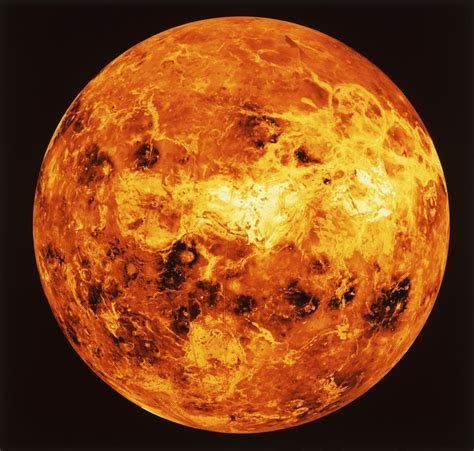
Venus
Secondly, It’s Venus! Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system due to its carbon dioxide atmosphere and clouds. It rains acid on Venus! The carbon dioxide and hot air are trapped in by the atmosphere, making it hotter than Mercury. It is also similar in size to earth.

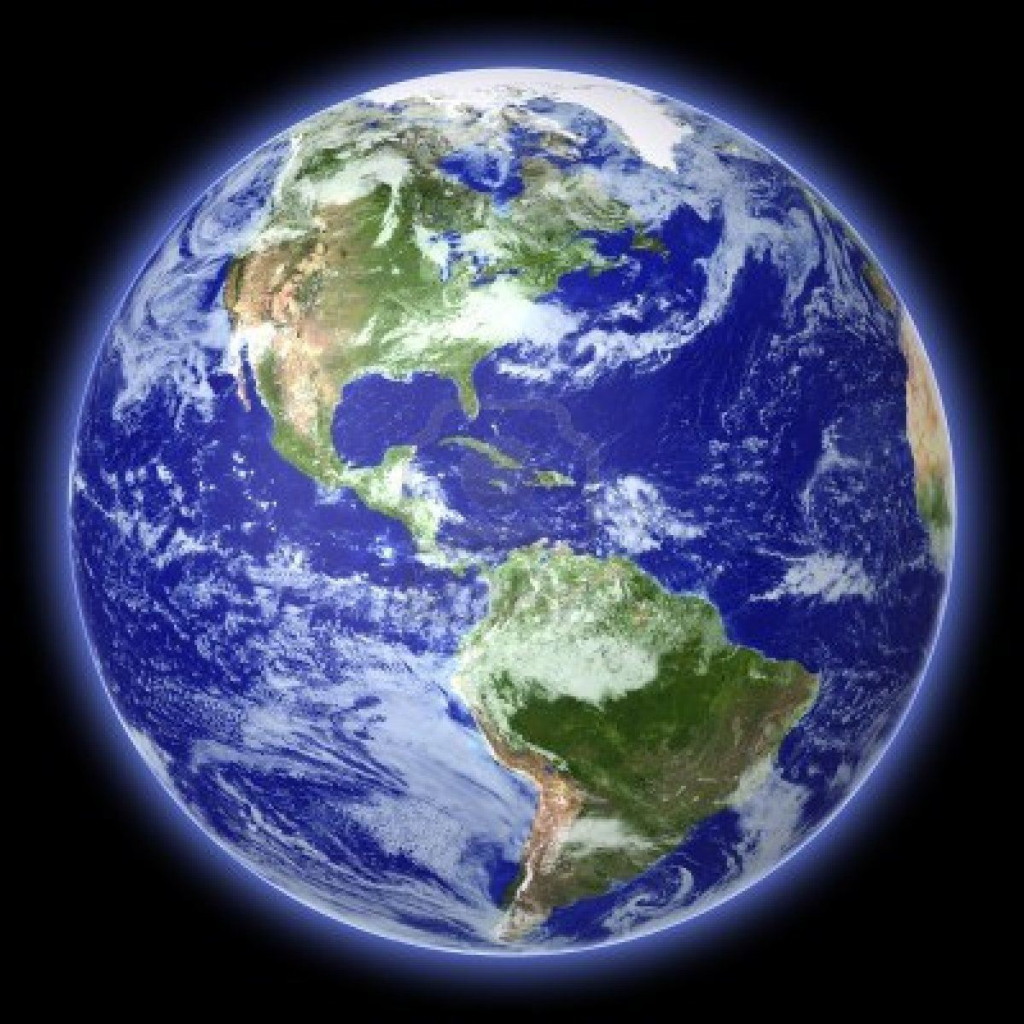
Earth
Next up is our home planet, Earth. Earth is the only planet to have existing water in the Solar System right now. In fact, it has water because It’s in the Goldilocks zone from the sun. (In the future, the sun will swell to an impressive size and swallow some planets. Mars will be in the goldilocks zone at that time.

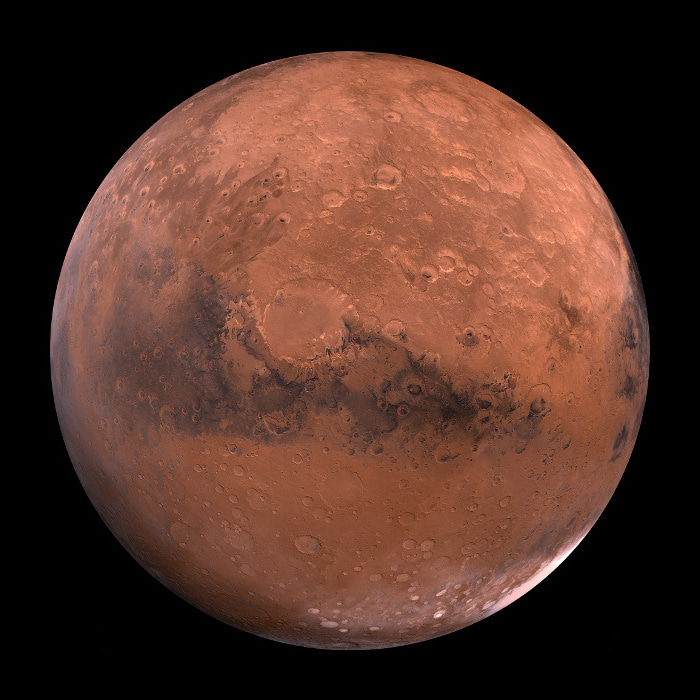
Mars
Hmm, what’s that little red dot hanging over there? Well, the only planet in the solar system that’s completely covered in iron oxide is Mars. Mars has the tallest mountain in the solar system, Olympus Mons. NASA is working on moving to mars these days.

Jupiter
After that red rocky planet, Jupiter is the next planet in line. The biggest planet in the solar system, weighing more than every planet’s weighted combined. This planet is the nearest planet to earth that has rings. (Yes, it has rings, but it’s really hard to see them.)
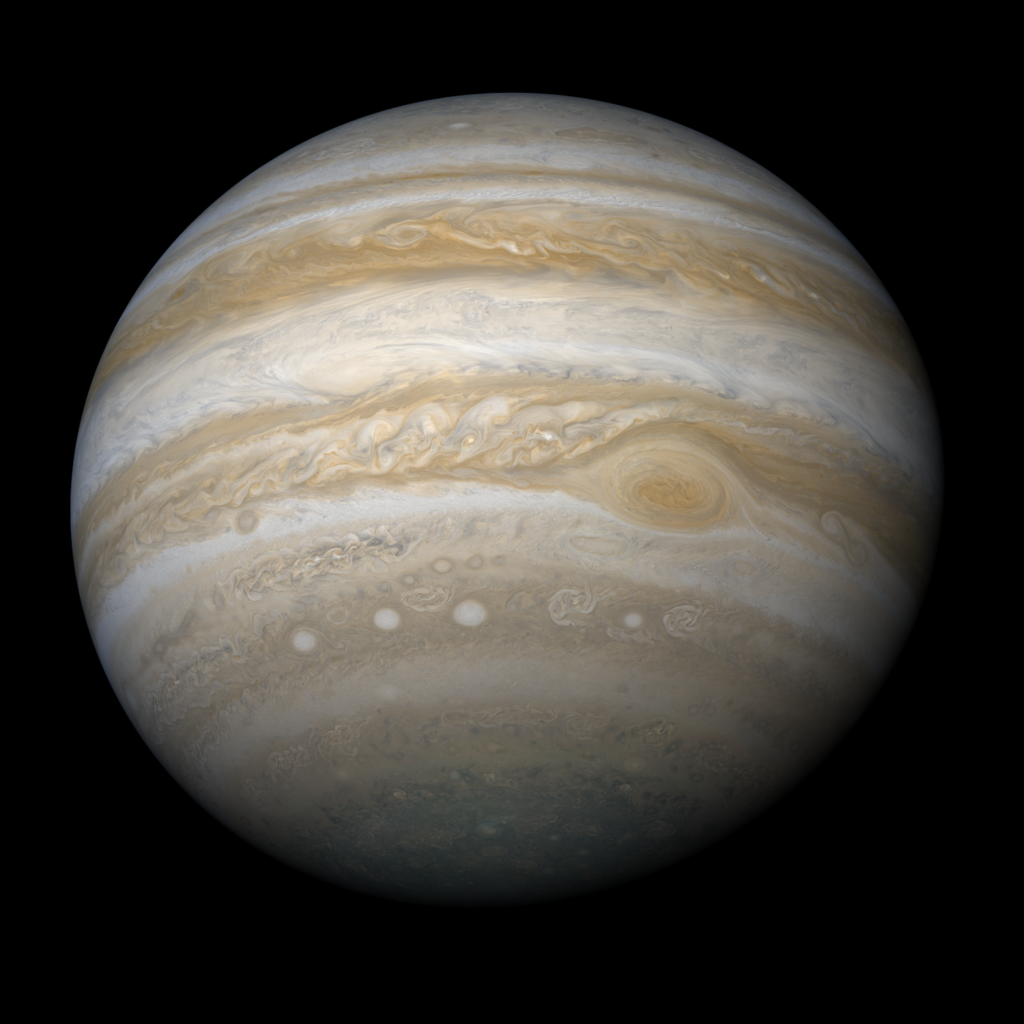

Saturn
The planet known for its rings is Saturn. In fact, it has 7 layers of rings, and outward from the planet in order is: D, C, B, A, F, G and E. Saturn is the second biggest planet in the solar system.
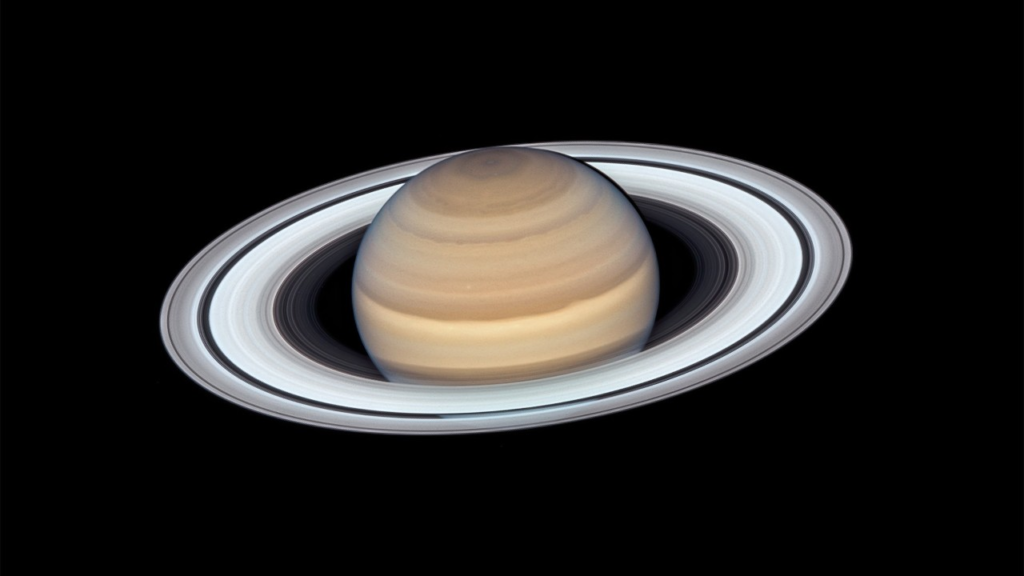

Uranus
The planet with the weirdest rotation ever, is Uranus. Some say that this phenomenon is due to a large space object impacting on the side of Uranus a long time ago. Uranus is the 2nd farthest planet from the sun.

Neptune
Finally, the outermost planet from the sun, is Neptune. Neptune is a gas giant, like all 4 outer planets. Neptune was found 234 years before it actually was called a planet, because this Astronomer did not realize that it was a planet.
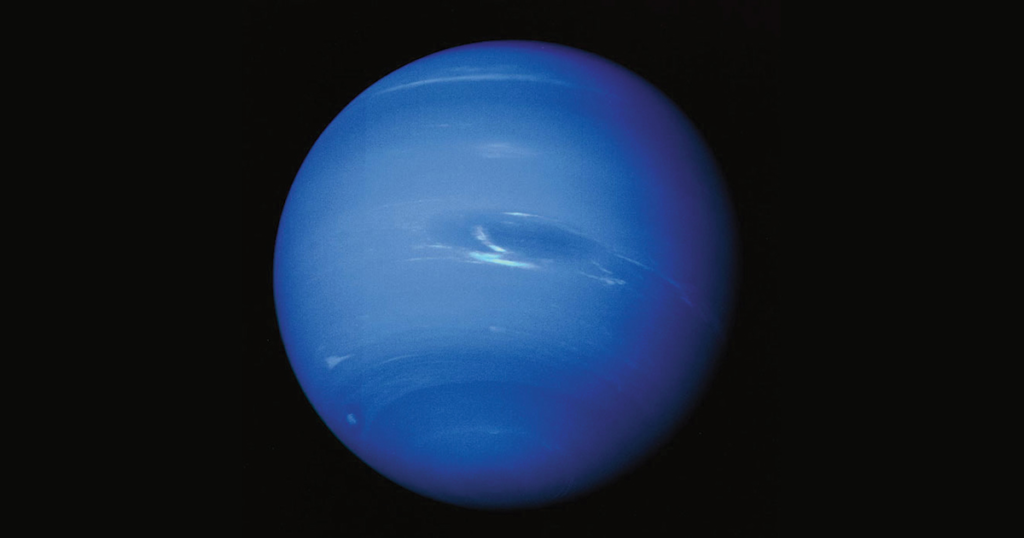

Asteroid Belt
The Asteroid Belt is between Mars and Jupiter, and Jupiter’s gravity usually prevents Mars’s gravity to fling asteroids to earth.
The Asteroid Belt is the closest belt to earth, and surprisingly, all of them are a couple miles apart, and you can fly through without encountering one.
I could not find a picture for the Asteroid Belt. But I could for an Asteroid:
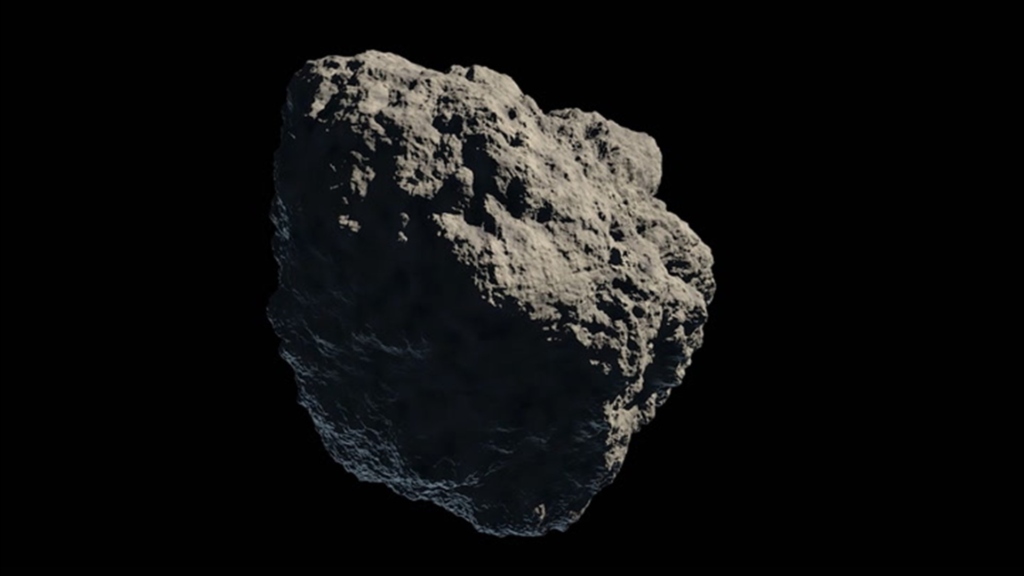

Kuiper Belt
What in the world is that ring around the solar system? It’s probably the Kupier Belt.
The Kupier Belt is a belt of comets, asteroids, and random pieces of ice. This is because it’s so far from the sun that random debris is sometimes ice. (I mean a layer around that piece of debris.)
I could not find a picture for the Kuiper Belt
Oort Cloud
The Oort Cloud is a weird cloud around the solar system that stretches a quarter way to the nearest sun. Most comets originate from the Oort Cloud.

Moons
Moons are also pieces of debris that fly by and get caught by the planet’s gravity. Earth has one, and the first person to step foot on it was Neil Armstrong. He also was watched Live on TV by over 500 million people.


Stars and Black Holes
The Birth and Death of a Sun
A star forms when a gas cloud, (usually left behind by a supernova) starts merging atoms into each other. It creates elements, and when they merge again and again, it eventually turns into a sun.
The Process Starts.
Elements within the sun’s core is pushing out to fuel the surface. Helium, Hydrogen, Sulfur, Magnesium, Iron, etc.
The Sun slowly expands due to the elements pushing out to fuel the sun’s surface, and the minerals are nearly exhausted. The sun gets bigger, and so does its gravity. At this point, all minerals are exhausted except for Iron. Iron tries to fuel the sun, so its gravity doesn’t destroy the sun.
Iron cannot fuel the sun, and as a result, the sun gets destroyed on its own gravitational force. It explodes into a supernova. Now it has two stages it can turn into: (It could also turn into a white dwarf, but the sun needs to originate from a medium-sized star to do that. Black Holes and Neutron Stars originate from Giant Stars.
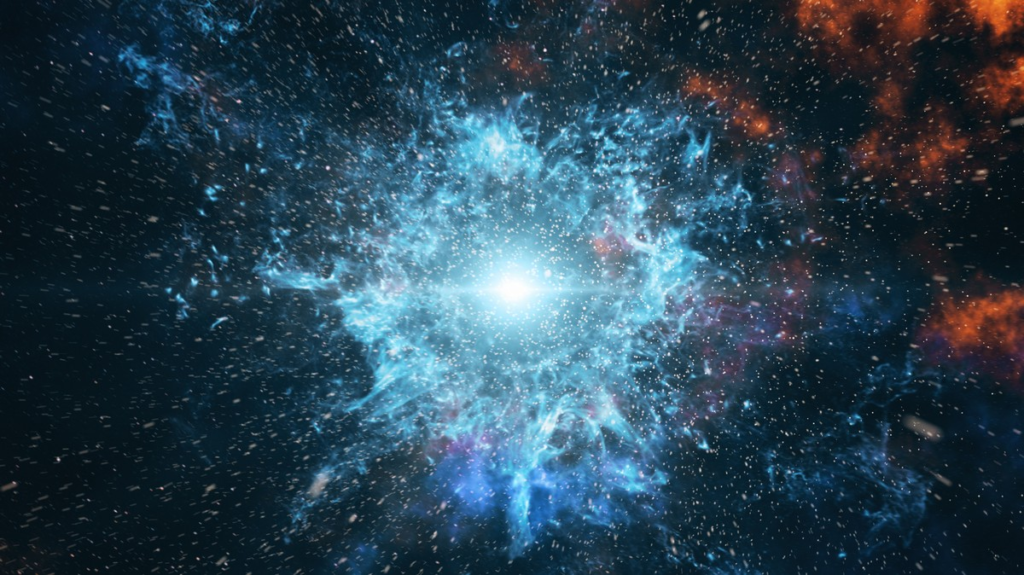

Black Hole
The supernova collapses into a singularity– a thing infinitely smaller than an atom but at the same time infinitely dense. The Supernova blows and expands out– making a gas cloud. Some of it is swallowed by the Black Hole. The singularity grows faster than ever and turns into a black hole. (In the middle of a black hole is a singularity.) Our sun needs to be 2 times bigger than it is at its max size to turn into a Black Hole. Black Holes are black because light cannot escape. (Light goes about 200,000 Miles Per Second.
Neutron Star
The supernova collapses into about the size of a city. (A lot of debris Explodes out really fast turning into a gas cloud, and some of it is swallowed by the Neutron Star.) It becomes extremely dense, (Less dense than a black hole) and can spin 700 – 800 times per second. The surface of a neutron star is also really smooth. Our sun needs to be 1.4 times bigger than it is at its max size to become a Neutron Star. Neutron Stars are so dense 1 teaspoon of it on earth would weigh 10 million tons.
Black Holes
Black Holes are nonstop growing objects in space, and one of my favorite things about space.
A Black Hole forms when a supernova (From a sun) explodes and collapses into a Black Hole.
Here are some facts!
- Some think that Black Holes die because of leaking heat and energy over time.
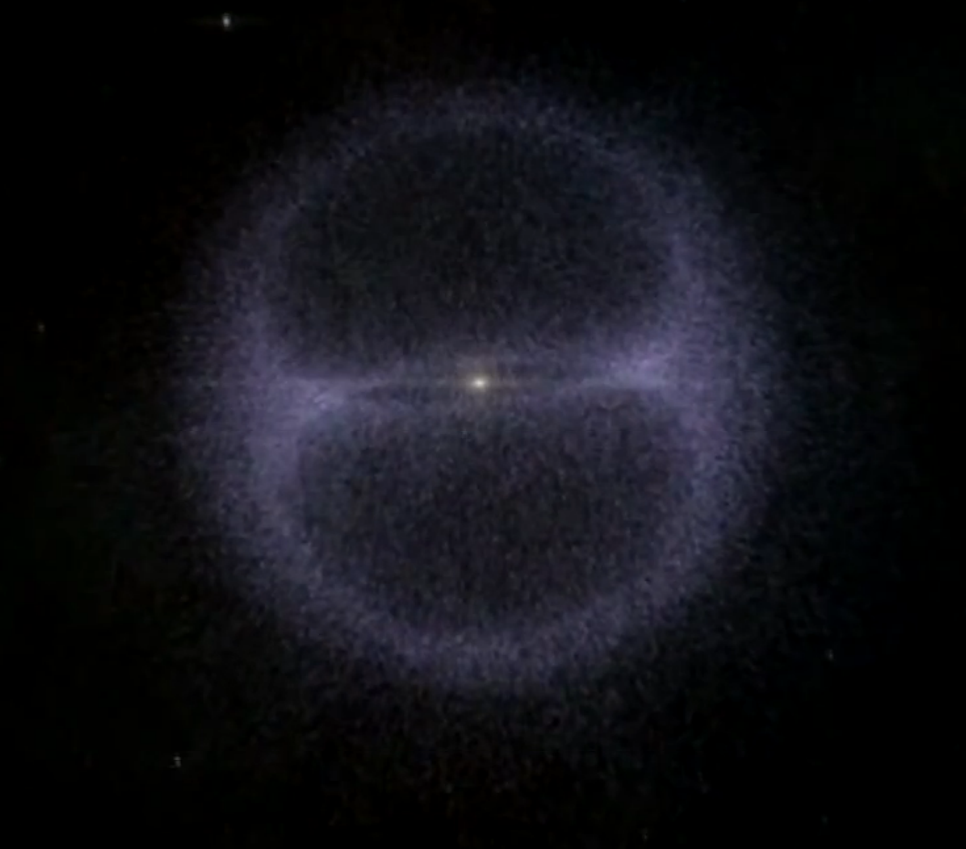
- Some Black Holes spin so fast– thousands of times per second! They spin so fast that they create that blue beam below in the picture.
- An Event Horizon of a Black Hole is the Boundary that if you cross then you will be sucked in. (Light cannot escape this Boundary.)
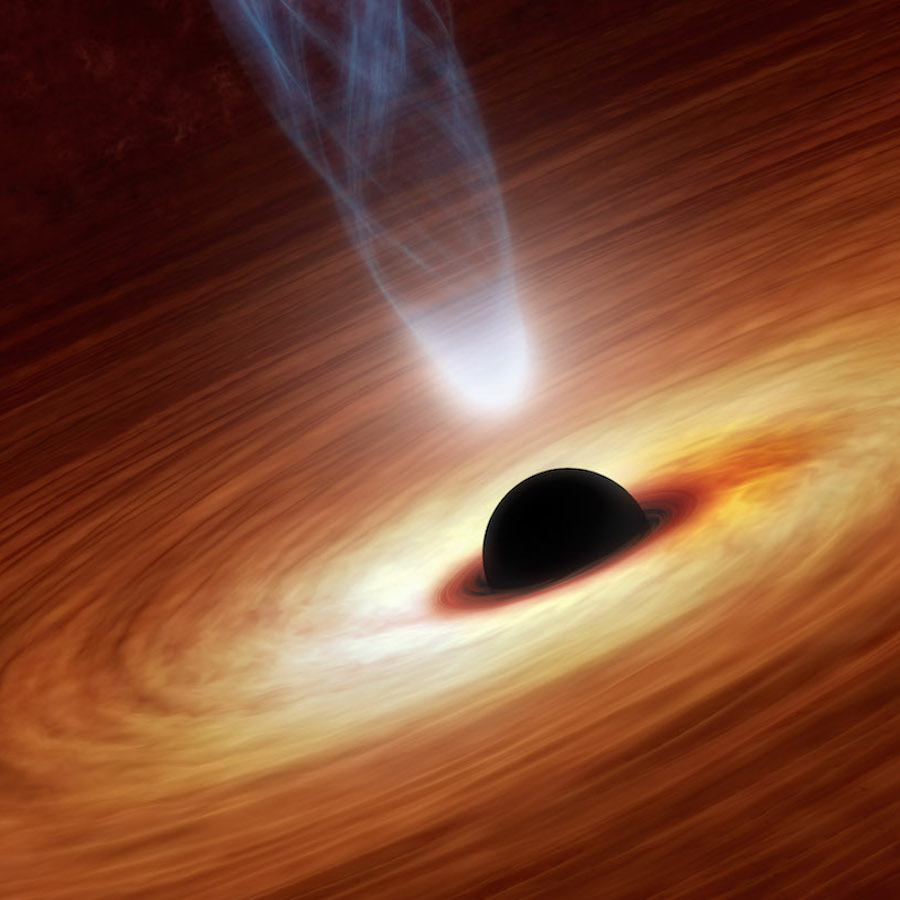

Supermassive Black Holes
Hmm, do you think this should be in the ‘Stars and Black Holes’ section? Well, yes, it can be in both. But why is it in Galaxies?
First of all, we need to look at what a Supermassive Black Hole is.
S E A R C H I N G. . . . . . . . . . . .
(One inch later)
Well, here’s the answer:
‘A Supermassive Black Hole is a giant Black Hole located in the center of Galaxies. These powerhouses help the galaxy survive. No galaxy can be there without a Supermassive Black Hole in the center.’
(I did not copy the text above, I made it myself.)
Now what? I guess a fact would do…
FACT: Supermassive Black Holes are usually 1 million times bigger than normal Black Holes. (Also known as Stellar Black Holes)

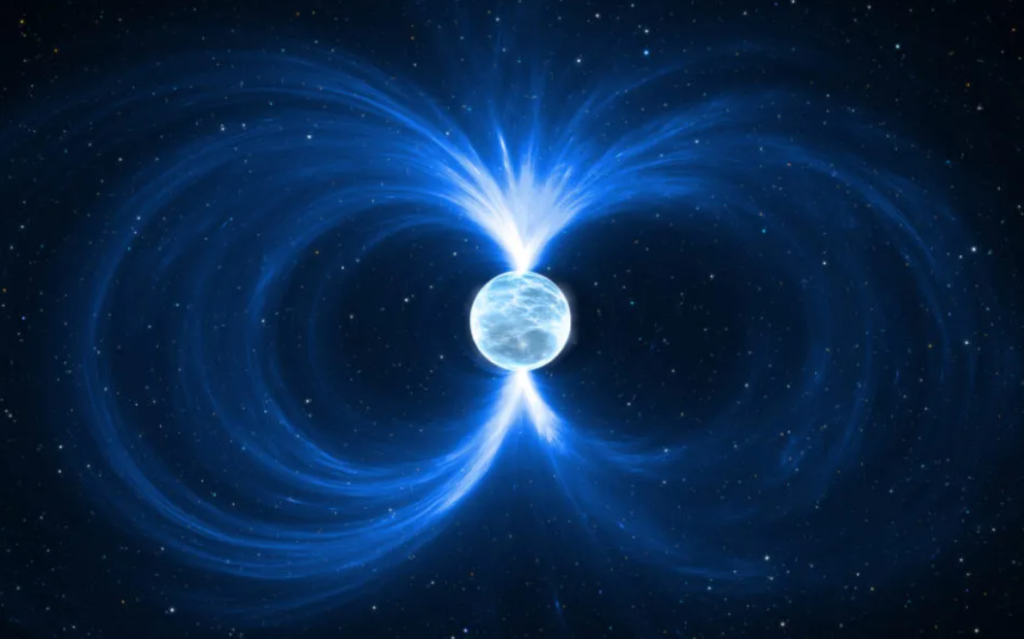
Neutron Stars
Neutron Stars are extremely dense, that they rotate 700 – 800 times per second, and one teaspoon of it on Earth could weigh 10 million tons.
Why does “one teaspoon of it on Earth could weigh 10 million tons.” Matter?
Why does when I say it, it has to be on Earth to weigh that much? Gravity.
Imagine you standing on a scale. (Person weight scale) and something is pushing you down. (Gravity) And if the thing pushing you down is stronger, then it weighs more.
Our Sun’s Life
A Sun is a massive ball of energy, containing elements that are also found on Earth. Like Helium, Hydrogen, Iron, Carbon, Oxygen, Silicon, Magnesium, Neon, Iron, Nitrogen, etc. (The Element most found in the sun is Hydrogen, followed by Helium.
Our Sun will turn into a white dwarf, after a supernova explosion. The sun will compress so much that its core becomes extremely dense, turning into a white dwarf.

Clusters
Galaxy Clusters
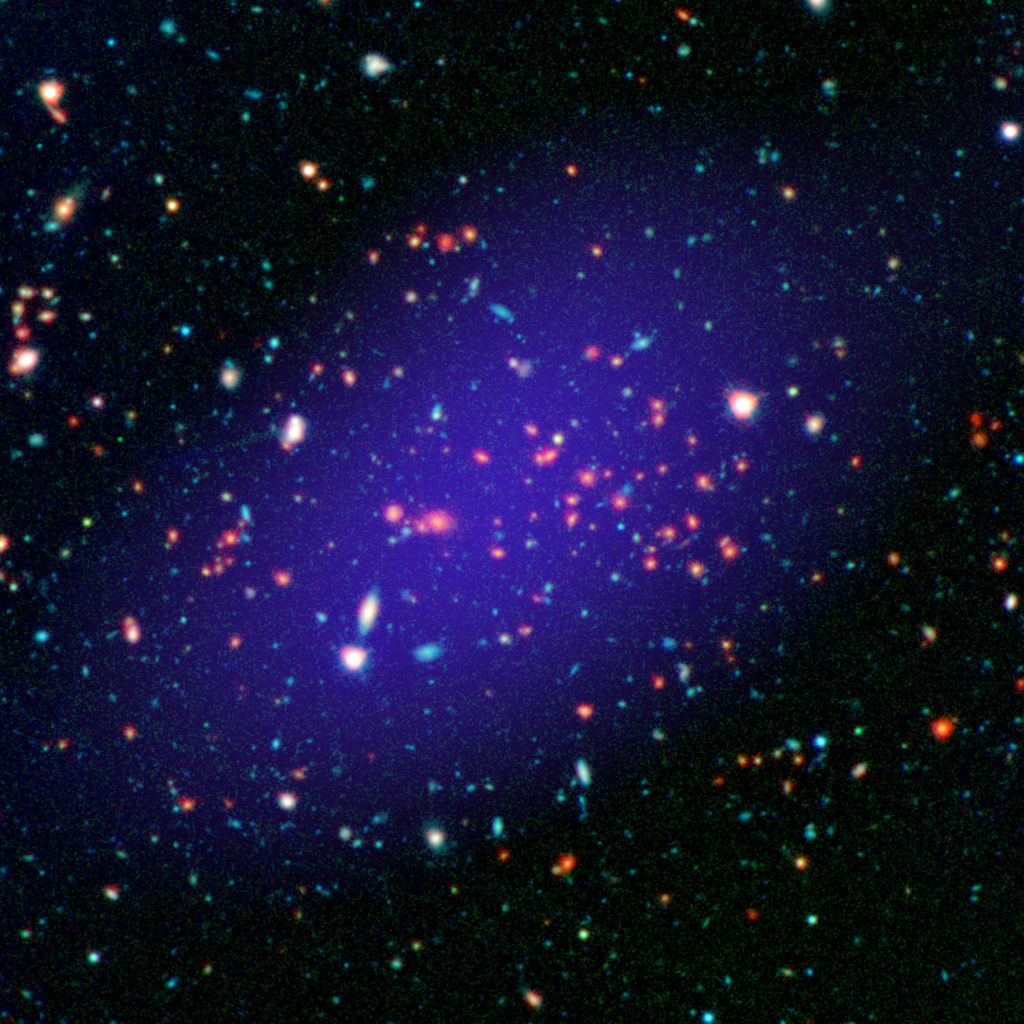
Galaxy Clusters are giant groups of galaxies close to each other to make a Galaxy Cluster. They are close to each other because of gravity pulling them together. There are many types of Galaxies:
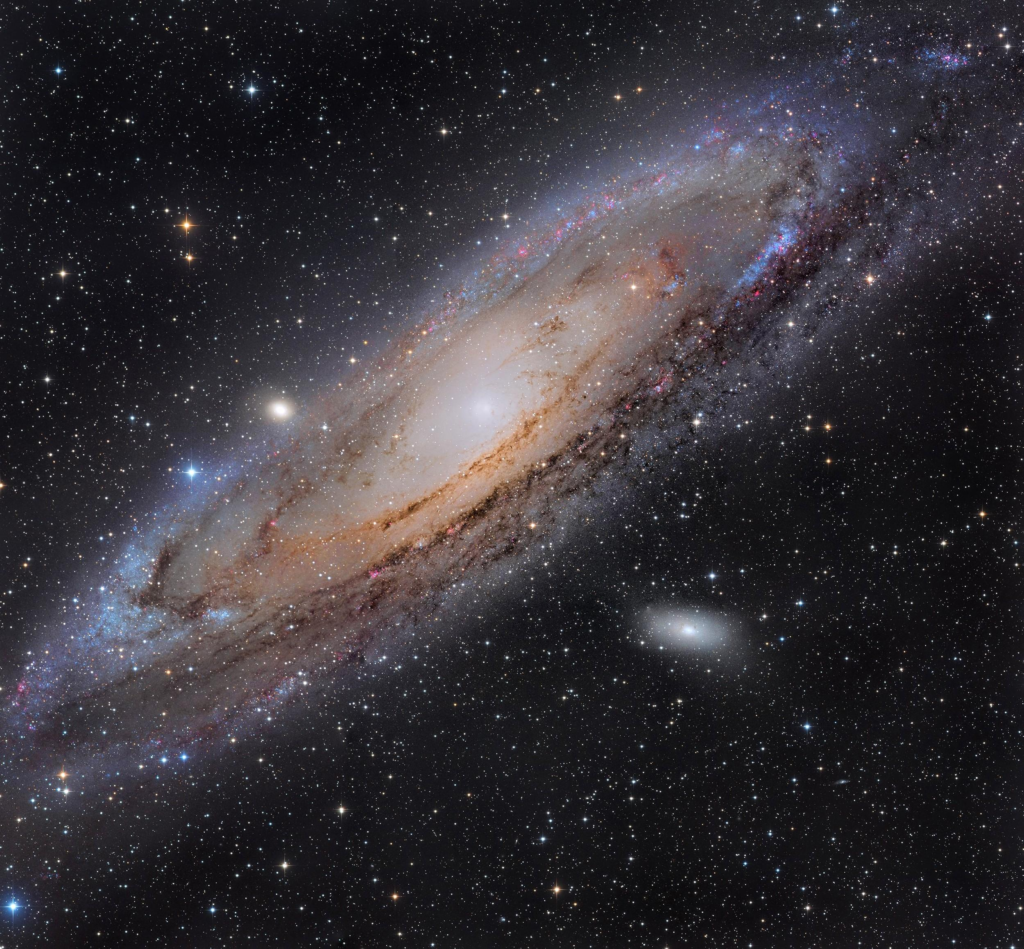




Imagine a ton of these in a group, which forms a Galaxy Cluster.

Sun Clusters
There are all types of suns, and, just like Galaxies, there are also clusters of them. Tons of these clusters make up a galaxy. (There are also Black Holes)
Just like Galaxies, they are attracted by gravity and sometimes, gravity lets go of a star, making it fly away into outer space. (A star flying away without it in a cluster is called a ‘Lonely Star’.)
Sun Clusters are like Galaxy Clusters, except that they have tons of swirling balls of energy, (Suns) in them. Galaxies in Galaxy Clusters are also really far apart.
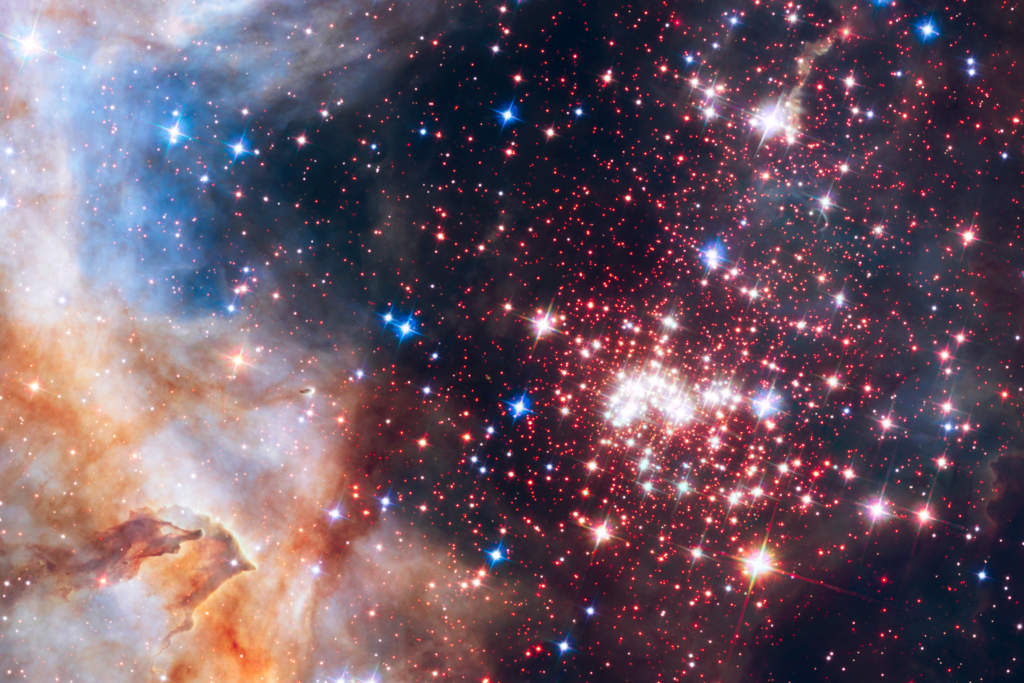

Galaxies
Galaxie Collisions
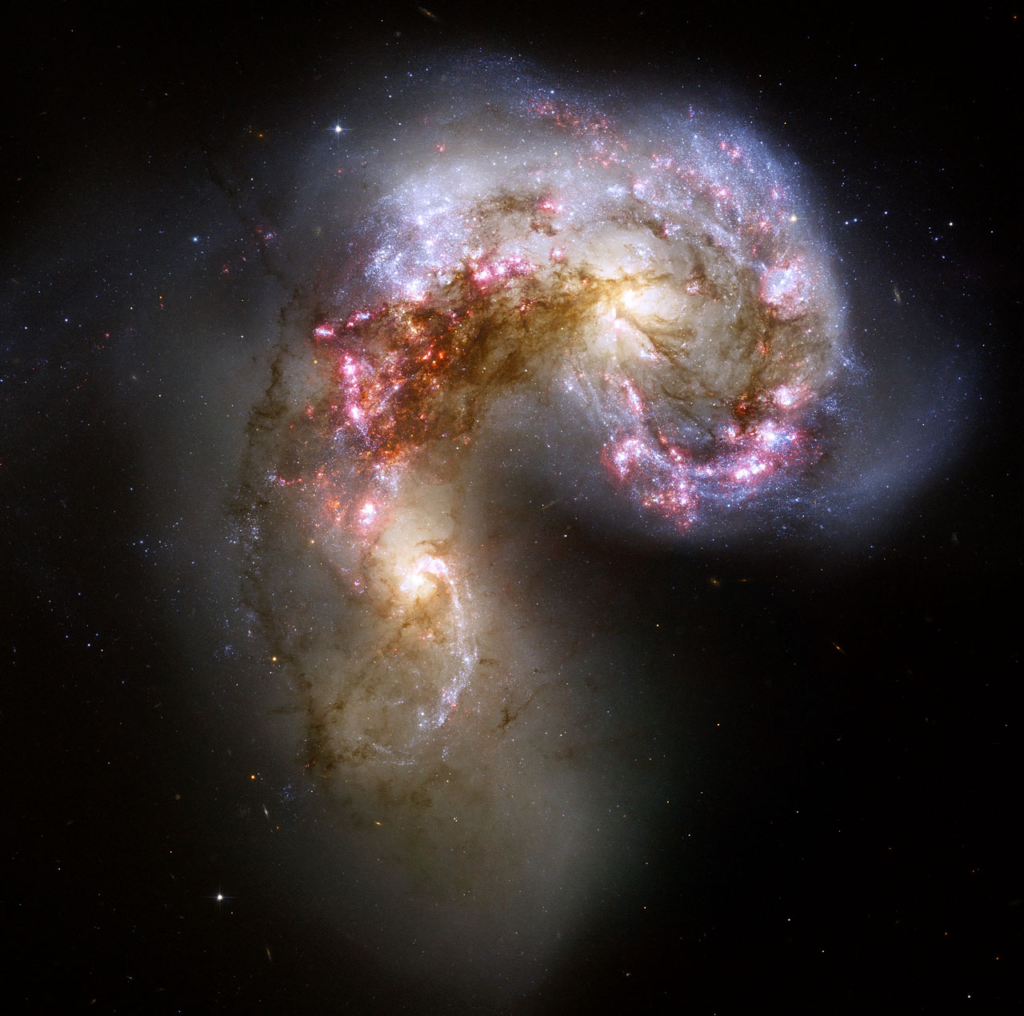
Our Milky Way galaxy is going to crash into the Andromeda Galaxy after a long period of time. When some galaxies crash into each other, sometimes galaxies can go through each other– this happens when both galaxies are aligned perfectly so that nothing crashes into each other.
But when a galaxy truly crashes into each other- they usually form an Irregular galaxy. You can scroll up a bit to see it, but why waste your time? Here’s a picture of an Irregular galaxy.
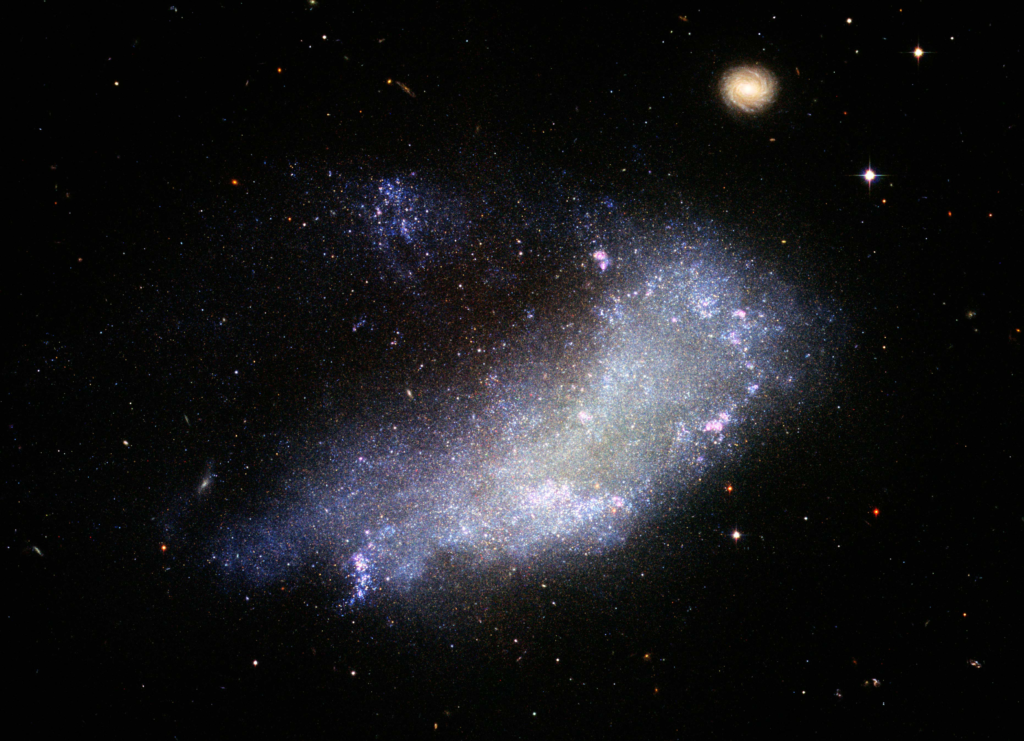

The Andromeda Galaxy is bigger than the Milky Way Galaxy.
If the two main Black Holes of the galaxies hit each other, the bigger one will swallow the smaller one, and destroy the other galaxy. The Andromeda Galaxy’s Supermassive Black Hole in the center of it is bigger than the Milky Way Galaxy’s Supermassive Black Hole. And the new galaxy will be an Irregular one, having already made a name: The Milkdromeda Galaxy.
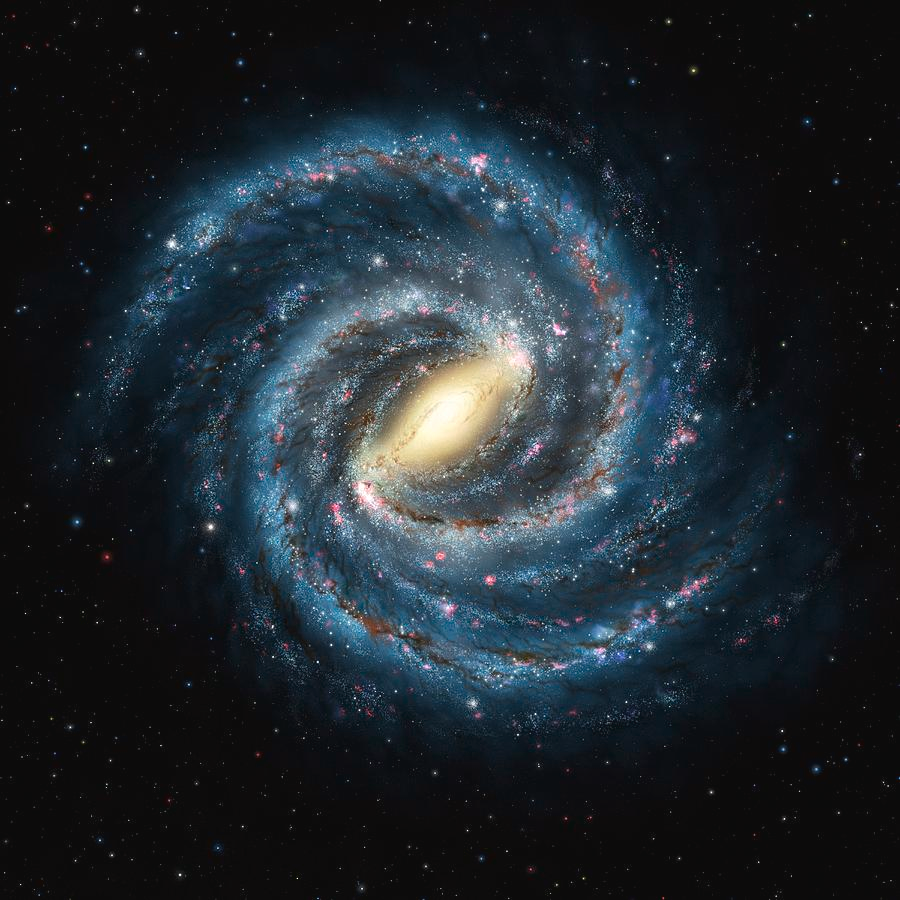
Our Galaxy – The Milky Way
Our home galaxy is no more than the Milky Way Galaxy, which is a Barred Spiral. The Milky Way Galaxy is roughly 120,000 light-years across, which light takes about 120,000 years to cross. (Light goes roughly 180,000 MPS. (Miles Per Second.)
The Milky Way Galaxy also belongs in a cluster named ‘The Local Group’ containing about 40 galaxies. Also, the Supermassive Black Hole in the middle of the Milky Way Galaxy is usually called ‘Sagittarius A’.

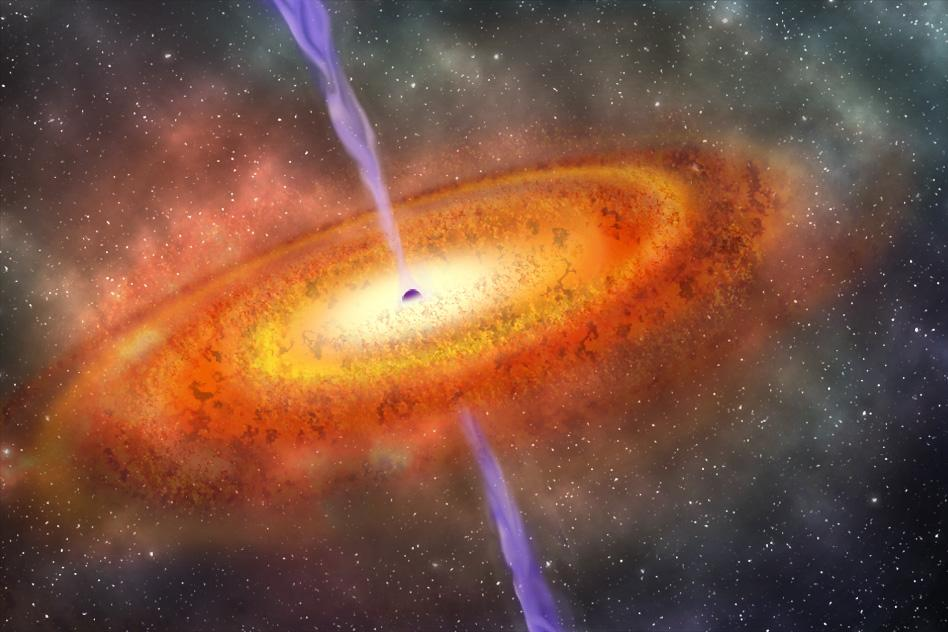
Supermassive Black Holes
Hmm, do you think this should be in the ‘Stars and Black Holes’ section? Well, yes, it can be in both. But why can it be in Galaxies?
First of all, we need to look at what a Supermassive Black Hole is.
S E A R C H I N G. . . . . . . . . . . .
(One inch later)
Well, here’s the answer:
‘A Supermassive Black Hole is a giant Black Hole located in the center of Galaxies. These powerhouses help the galaxy survive. No galaxy can be there without a Supermassive Black Hole in the center.’
(I did not copy the text above, I made it myself.)
Now what? I guess a fact would do…
FACT: Supermassive Black Holes are usually 1 million times bigger than normal Black Holes. (Also known as Stellar Black Holes)

The Big Bang
The universe started approximately 13 billion years ago and is still expanding today. it will keep on expanding forever.
However, a theory states that soon, the universe will stop expanding, it will shrink. Shrink into something so small that it will make another big bang, forming a new universe. The theory also says that there will be an infinite number of universes after us, and there have been infinite universes before us.
Although, this theory also doesn’t make sense. In our universe, everything is spread out equally. While if there was an explosion, things would have been spread out unevenly.
Can you make a theory? Will the mystery of the Big Bang be solved before humans are extinct? Will spaceships in the future be able to get too far away suns, planets, and other space objects?

Comment below your answers to these questions. Here are some more questions: Will we find aliens in the future? Will we survive the supernova of the sun? Will we manage to colonize Mars? You can give all the answers to these questions in the comments below!